Vietnam FDI Entry Handbook 2025: A Practical Guide for EMEA SMEs
14/07/2025
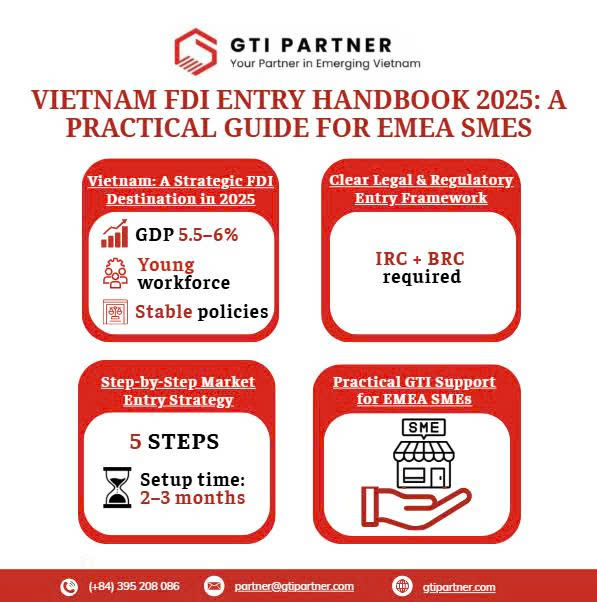
Why Vietnam in 2025?
- Vietnam remains a top FDI destination with 5.5%–6% GDP growth, a young workforce, and stable policies.
- Participation in RCEP, CPTPP, EU-Vietnam FTA reduces tariffs and eases market access.
- Key sectors: manufacturing, renewable energy, IT services, and consumer goods.
Key Data:
- Population: ~100 million.
- Median age: 32.5 years.
- Consistent FDI growth in electronics, green energy, and logistics.
Vietnam’s FDI Legal Landscape
- Investment Law 2020 governs foreign investments.
- Foreign investors must obtain:
- Investment Registration Certificate (IRC).
- Business Registration Certificate (BRC).
- Common business forms:
- Representative Office (market research, non-revenue).
- Limited Liability Company (LLC).
- Joint Ventures for regulated sectors.
- Tax compliance includes CIT (20%), VAT (10%), and import/export procedures.
Tip: Always conduct legal reviews and use bilingual contracts.
For a comprehensive overview, download Guide to Doing Business in Vietnam (PDF) — including legal setup options, FDI strategies, and growth insights for 2025.
Step-by-Step Market Entry Plan
Step 1: Feasibility Study and Market Research
- Analyze demand, competitors, pricing, and regulatory challenges.
- Evaluate industrial zones, logistics infrastructure, and human resources.
Step 2: Selecting the Entry Mode
- Choose Representative Office, LLC, or JV based on sector and objectives.
Step 3: Licensing and Compliance
- File for IRC and BRC with the Department of Planning and Investment.
- Check if sector-specific licenses are needed (e.g., education, logistics).
Step 4: Building Local Partnerships
- Identify suppliers, distributors, or JV partners.
- Perform due diligence and relationship building.
Step 5: Operational Setup and Hiring
- Draft internal policies aligned with Vietnam’s Labor Code.
- Set up accounting, tax reporting, and HR processes.
Sector Spotlights
✓ Manufacturing: Vietnam’s competitive costs attract EMEA SMEs seeking China+1 strategies.
✓ Renewable Energy: Opportunities in solar, wind, and waste-to-energy with Vietnam’s net-zero targets.
✓ IT & Digital Services: Cost-effective outsourcing and growing tech talent pool.
✓ Consumer Goods: Rising middle class drives demand for quality imports and retail expansion.
Practical Considerations for SMEs from Europe and the Middle East
- Cultural factors: Build relationships through face-to-face meetings.
- Currency: Vietnamese Dong (VND); plan for repatriation processes.
- Timeframe: Setup can take 2–3 months; plan for realistic entry.
- Contracts: Use bilingual agreements reviewed by local counsel.
Compliance and Tax Overview
- Corporate Income Tax (CIT): 20% standard rate.
- VAT: 10% standard rate.
- Withholding Tax: Applies on cross-border payments.
- Customs: Comply with import/export licensing and HS code classifications.
Common Challenges and How to Avoid Them
- Underestimating administrative timelines. Work with local experts.
- Choosing the wrong entity structure. Align with your long-term plans.
- Cultural misalignment. Invest time in relationship-building.
- Overlooking hidden costs. Budget for compliance, HR, and legal advisory.
How GTI Partner Can Support Your Vietnam Entry
GTI Partner specializes in helping EMEA SMEs expand into Vietnam with:
- Market feasibility and tailored entry strategies
- Licensing and compliance navigation and support
- Partner sourcing, due diligence and agreement
- One-time or ongoing operational and HR support
- Sector-specific consulting in manufacturing, Real Estate, and IT
- Sales outsourcing, local representation and presence
Next Steps: Your Vietnam FDI Checklist
✓ Validate your market and product fit.
✓ Determine your preferred entry mode.
✓ Plan your licensing and compliance path.
✓ Build trusted local partnerships.
✓ Set up financial, HR, and operational systems.
✓ Engage a local advisor for on-the-ground execution.
👉 Contact GTI Partner to receive your customized go-to practical guide for your EMEA SME market entry and expansion into Vietnam.
GTI Partner | Your Trusted Vietnam Market Entry Advisor